5GC Communication Models A, B, C and D
The 5th generation of mobile core networks (5GC) implement Service Based Interface (SBI) APIs for the Control Plane (CP) part of the system [1], following Service-Oriented Architecture (SOA) and Microservices principles. One of the main goals of this architecture is to achieve loose coupling which has multiple impacts on the system’s resiliency, performance, flexibility and security.
- Model A: Direct communication without NRF interaction
- Model B: Direct communication with NRF interaction
- Model C: Indirect communication without delegated discovery
- Model D: Indirect communication with delegated discovery
- References
- Credits
The service discovery function in this architecture is performed by a component called Service Registry. In the context of the 5GC, the service registry component is called Network Repository Function (NRF). Service Provider Network Functions (NF) would register with the NRF, whereas Service Consumer NFs would send discovery requests to the NRF to find active/suitable provider NFs.
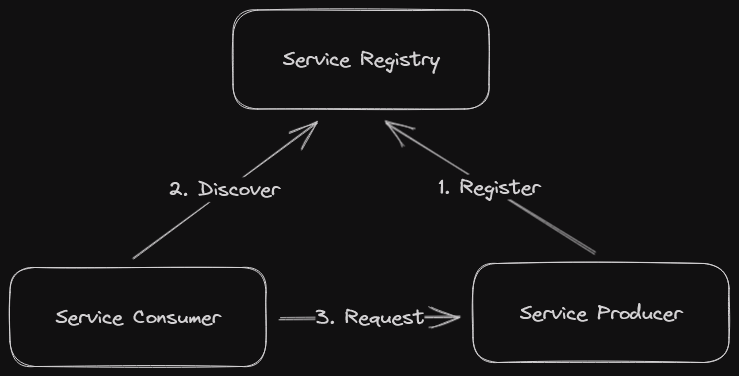
Registration requests, discovery requests and communications between service consumers and service providers may or may not be routed through a communication broker called Service Communication Proxy (SCP).
The combination of both NRF and SCP in the 5GC generates 4 different Communication models for NF/NF services interaction [2]. The following table details the entity that is responsible of each step of the communication process.
| Communication Model | A | B | C | D |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NF register | No NRF, No SCP | NRF | NRF | NRF |
| NF discover | No NRF, No SCP | NRF | NRF | SCP |
| NF selection | NF consumer | NF consumer | NF consumer or SCP | SCP |
| NF Service Request | Direct | Direct | via SCP | via SCP |
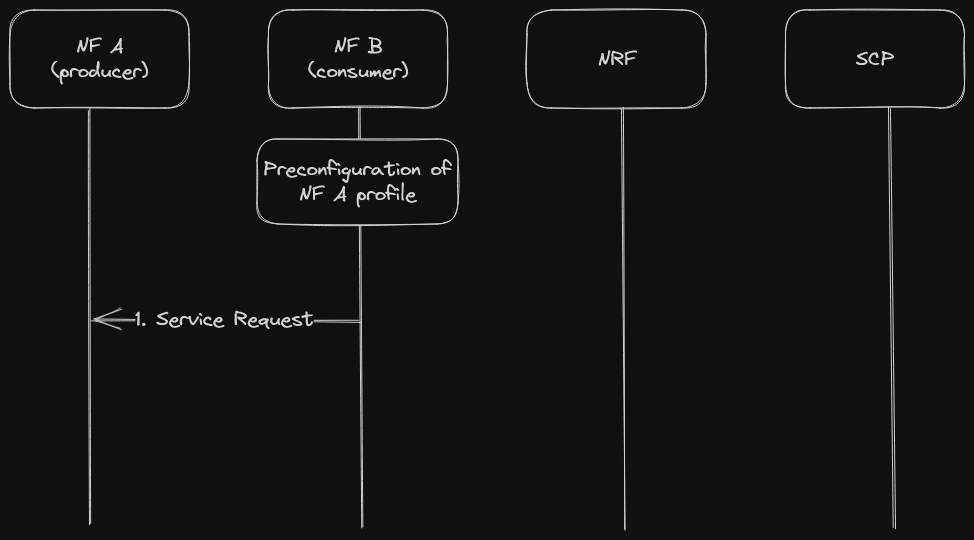
Model A: Direct communication without NRF interaction
Neither NRF nor SCP are used. Consumers are configured with producers’ “NF profiles” and directly communicate with a producer of their choice [2].
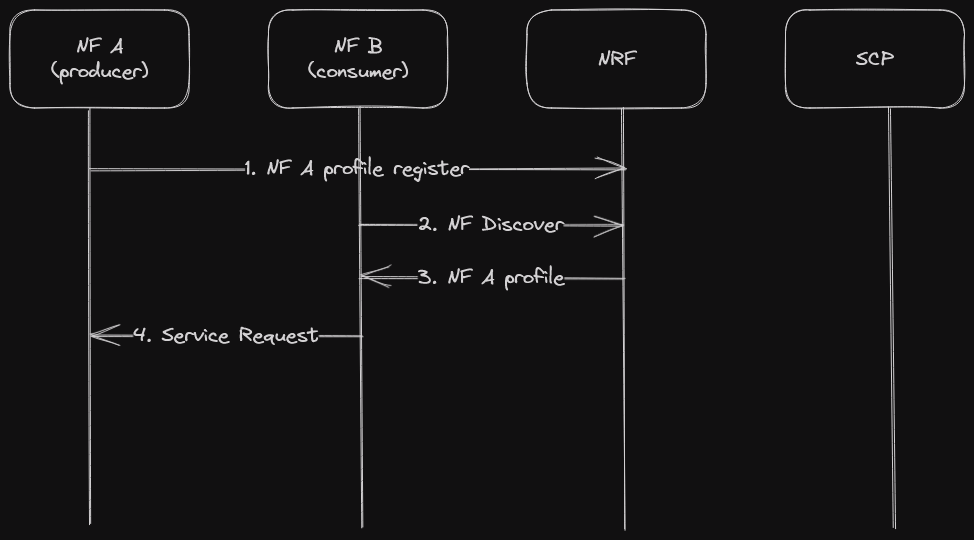
Model B: Direct communication with NRF interaction
Consumers do discovery by querying the NRF. Based on the discovery result, the consumer does the selection. The consumer sends the request to the selected producer [2].
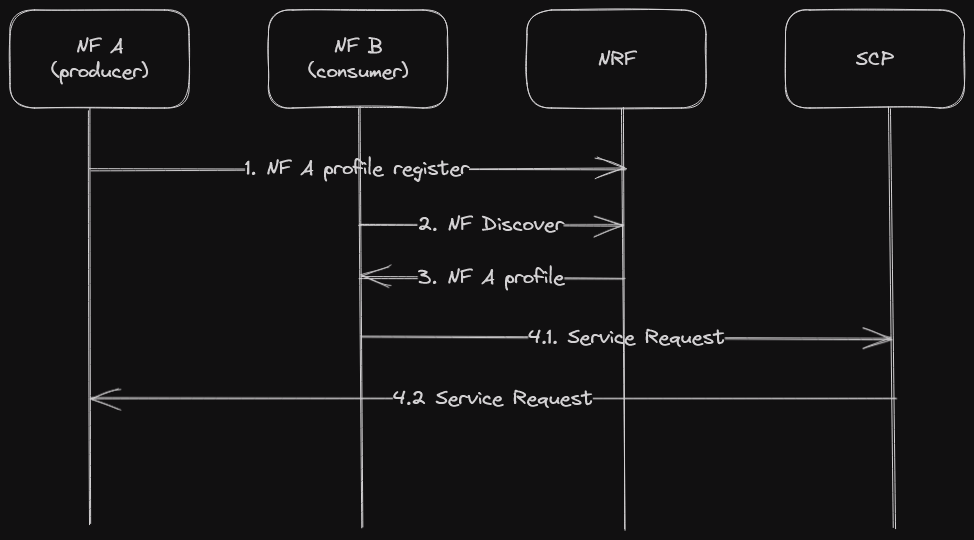
Model C: Indirect communication without delegated discovery
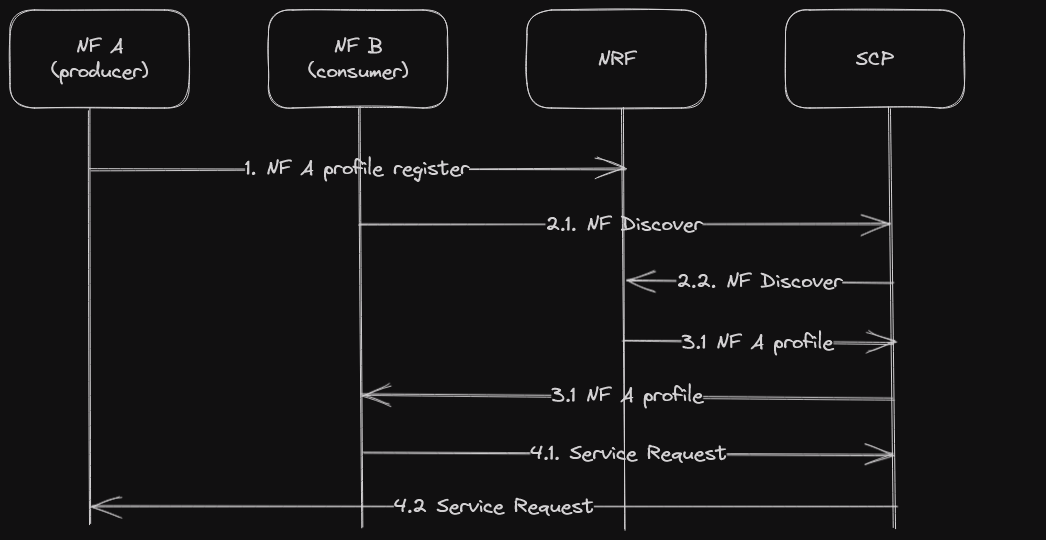
Consumers do discovery by querying the NRF. Based on discovery result, the consumer does the selection of an NF Set or a specific NF instance of NF set. The consumer sends the request to the SCP containing the address of the selected service producer pointing to a NF service instance or a set of NF service instances. In the latter case, the SCP selects an NF Service instance. If possible, the SCP interacts with NRF to get selection parameters such as location, capacity, etc. The SCP routes the request to the selected NF service producer instance [2].
Model D: Indirect communication with delegated discovery
Consumers do not do any discovery or selection. The consumer adds any necessary discovery and selection parameters required to find a suitable producer to the service request. The SCP uses the request address and the discovery and selection parameters in the request message to route the request to a suitable producer instance. The SCP can perform discovery with an NRF and obtain a discovery result [2].
References
[1] 3GPP TS 29.501 version 15.5.0 Release 15
[2] 3GPP TS 29.501 version 16.6.0 Release 16
Credits
Thanks sofianinho for the nice feedback