On 5G Mobile Private Networks
Diving into the realm of 5G Mobile Private Networks, seeking to understand their potential, enablers and deployment models.
What is a 5G Mobile Private Network ?
A 5G Mobile Private Network (MPN), also known as a 5G Private Network or simply a Private 5G Network, is a dedicated wireless network infrastructure built using 5G technology to serve the specific needs of a single organization or entity. Unlike traditional mobile networks that are designed to serve the general public, private 5G networks are tailored to the requirements of a particular enterprise, industry, or campus environment.
Key features and characteristics of 5G MPNs include:
-
Dedicated Infrastructure: A private 5G network typically consists of dedicated hardware, including base stations (gNodeBs), core network components, and management systems, deployed and managed exclusively for the organization’s use
-
Customized Coverage: Private 5G networks offer customizable coverage and capacity tailored to the specific needs of the organization’s operational environment. This allows for optimized network performance and reliability within the premises
-
High Bandwidth and Low Latency: Leveraging 5G technology, private networks can deliver high-speed data transmission and ultra-low latency, enabling real-time communication, mission-critical applications, and IoT deployments
-
Secure and Isolated: Private 5G networks provide enhanced security and privacy features, including encryption, authentication, and access controls, to safeguard sensitive data and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements. These networks are isolated from public networks, reducing the risk of external threats
-
Customized Services and Applications: Organizations can develop and deploy custom applications and services optimized for their operational needs, leveraging the high-performance capabilities of private 5G networks. This enables innovation, efficiency improvements, and new business opportunities
-
Industry Applications: Private 5G networks are particularly suited for industries and use cases requiring reliable, high-bandwidth connectivity in challenging environments, such as manufacturing, logistics, healthcare, transportation, utilities, and smart cities
5G MPN enablers
5G Mobile Private Networks (MPNs) are enabled by several key technologies, including edge computing, lightweight 5G mobile networks, and automation.
-
Edge Computing: Edge computing brings computational resources closer to the data source, reducing latency and enabling faster processing of data. In the context of 5G MPNs, edge computing plays a crucial role in supporting real-time applications and services. By deploying control and compute nodes within the private network infrastructure, organizations can process data locally, near the point of generation, without having to send it to centralized data centers. This is especially important for latency-sensitive applications such as industrial automation, augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and autonomous vehicles.
-
Lightweight 5G Mobile Networks: Lightweight 5G mobile networks are optimized for deployment in specific environments, such as industrial plants, campuses, or enterprise facilities. These networks are designed to be flexible, scalable, and efficient, providing high-speed connectivity with minimal infrastructure footprint. Lightweight 5G networks leverage technologies such as small cells, dynamic spectrum allocation, and network slicing to deliver tailored connectivity solutions for diverse use cases within the private network environment. MPNs allow organizations to extend coverage, increase capacity, and support a wide range of IoT devices, sensors, and applications while minimizing deployment costs and complexity.
-
Automation: Finally, automation plays a critical role in the operation and management of 5G MPNs, enabling efficient resource allocation, optimization, and self-healing capabilities. Automation technologies such as network orchestration, and machine learning algorithms automate various network tasks, including network configuration, monitoring, and troubleshooting. Automated MPNs deployment and Life Cycle Management reduces manual intervention, and improves overall network efficiency and reliability.
MPN Deployment Options
A mobile network as 2 main blocs:
-
Control Plane (CP): which is responsible for managing signaling, control, and management functions. It handles tasks such as network setup, configuration, session establishment, mobility management, and policy enforcement. NFs such as Access and Mobility Management Function (AMF), Session Management Function (SMF), Policy Control Function (PCF), etc. form the CP.
-
User Plane (UP): which is responsible for the forwarding and processing of user data packets. It handles the transmission and reception of data between end-user devices (such as smartphones, IoT devices) and network services or applications. The UP is focused on efficient data delivery, packet forwarding, traffic optimization, and Quality of Service (QoS) enforcement. Radio Access Network (RAN) elements (e.g. 5G gNodeB) and User Plane Function (UPF) are part of the UP.
This architecture gives different deployment options that can be devided into two main families:
All-in-One Deployment
In this option, all network functions from both CP and UP, are consolidated into a single physical or virtualized appliance, commonly referred to as a “Network-In-a-Box”. This approach simplifies deployment and management by providing a compact, integrated solution that includes all necessary hardware and software components.
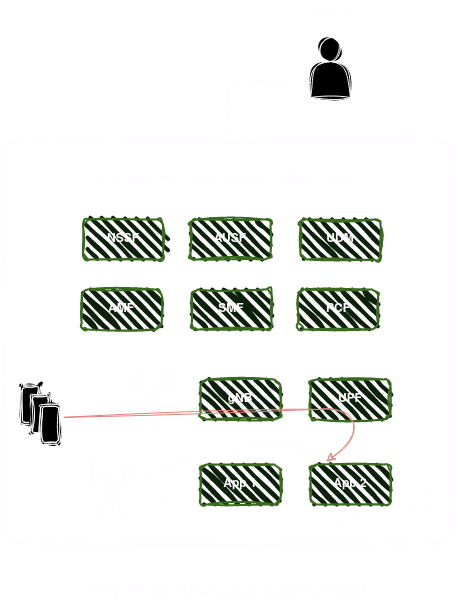
Hybrid Deployment - option a.
In this option, the CP is deployed on a central cloud (i.e. operator’s cloud, or public cloud). The UP is fully deployed on-premise.
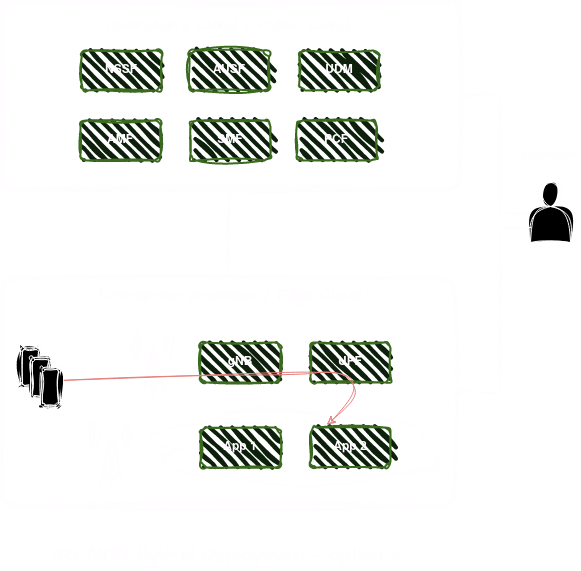
Hybrid Deployment - option b.
In this option, two UPFs are deployed, one on-premise and another in the central cloud. The on-premise UPF is deployed within the enterprise premises, closer to the edge devices and applications. This UPF is responsible for local breakout of traffic destined for enterprise edge cloud applications. The central cloud UPF provides connectivity to external networks, including the public internet. This UPF is dedicated to handling internet-bound traffic from enterprise devices and applications that require access to external services, websites, or public cloud-based resources
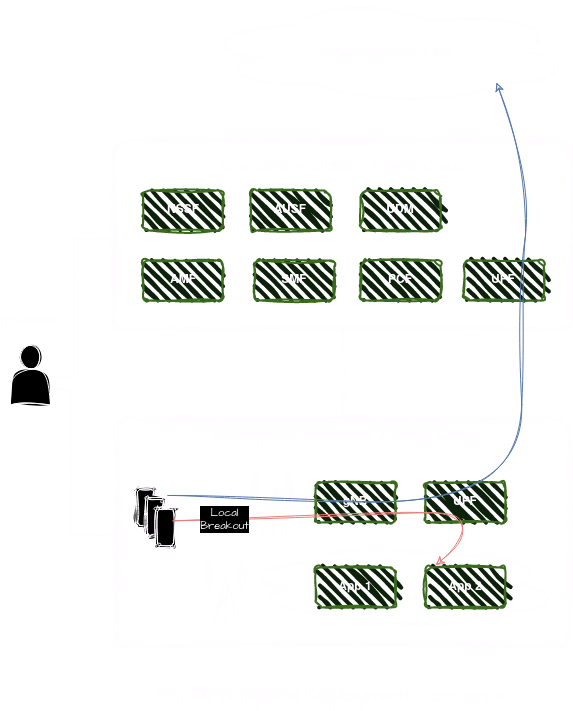
In this hybrid deployment model, the combination of on-premise and central cloud UPFs allows enterprises to optimize traffic routing, minimize latency, and ensure efficient utilization of network resources for both internal and external communication needs. By leveraging multiple UPFs strategically deployed across the network infrastructure, organizations can achieve a balance between local data processing, centralized management, and secure internet access, aligning with their specific business requirements and network architecture preferences.
Not only traditional Network Equipement Providers (NEPs) are building 5G MPNs, emerging players are also building MPN products using Open Source software, such as:
- BubbleRAN - private 4G/5G core network based on OpenAirInterface
- OAIBOX - private 5G core network based on OpenAirInterface
- Saviah - private 5G core network based on Free5GC
- firecell - private 4G & 5G core networks based on OpenAirInterface
- 5-fi - 5G private core network based on OpenAirInterface
- sysmocom - 3G & 4G private core networks based on Osmocom
- NeoPlane - private 4G & 5G core networks based on Open5GS
Credits
Figures made with ❤️ using draw.io